| [1] Zhao N,Roesler S,Kissel T.Synthesis of a new potential biodegradable disulfide containing poly(ethylene imine)- poly(ethylene glycol) copolymer cross-linked with click cluster for gene delivery.Int J Pharm.2011;411(1-2):197-205.
[2] Zhang G,Liu J,Yang Q,et al.Disulfide-Containing Brushed Polyethylenimine Derivative Synthesized by Click Chemistry for Nonviral Gene Delivery. Bioconjug Chem. 2012;23(6): 1290-1299.
[3] Lungwitz U,Breunig M,Blunk T,et al.Polyethylenimine-based non-viral gene delivery systems. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2005; 60(2):247-266.
[4] Breunig M, Lungwitz U, Liebl R, et al. Gene delivery with low molecular weight linear polyethylenimines.J Gene Med. 2005; 7(10):1287-1298.
[5] Neu M,Fischer D,Kissel T.Recent advances in rational gene transfer vector design based on poly(ethylene imine) and its derivatives.J Gene Med.2005;7(8):992-1009.
[6] Lungwitz U,Breunig M,Liebl R,et al.Methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)--low molecular weight linear polyethylenimine-derived copolymers enable polyplex shielding.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008;69(1):134-148.
[7] Peng Q,Zhong Z,Zhuo R.Disulfide cross-linked polyethylenimines (PEI) prepared via thiolation of low molecular weight PEI as highly efficient gene vectors. Bioconjug Chem.2008;19(2):499-506.
[8] Son S,Singha K,Kim WJ.Bioreducible BPEI-SS-PEG-cNGR polymer as a tumor targeted nonviral gene carrier. Biomaterials.2010;31(24):6344-6354.
[9] Koo H,Jin GW,Kang H,et al.Biodegradable branched poly(ethylenimine sulfide) for gene delivery. Biomaterials. 2010; 31(5):988-997.
[10] Choi S,Lee KD.Enhanced gene delivery using disulfide-crosslinked low molecular weight polyethylenimine with listeriolysin o-polyethylenimine disulfide conjugate. J Control Release.2008;131(1):70-76.
[11] Feng FL,Li RR,Zhang QY,et al.Preparation of reduction- triggered degradable microcapsules for intracellular delivery of anti-cancer drug and gene.Polymer. 2014; 55(1):110-118.
[12] Yang M,Cheng K,Qi S,et al.Affibody modified and radiolabeled gold-iron oxide hetero-nanostructures for tumor PET, optical and MR imaging. Biomaterials.2013;34(11):2796-2806.
[13] Guo J,Yang W,Wang C.Magnetic colloidal supraparticles: design, fabrication and biomedical applications.Adv Mater. 2013;25(37):5196-5214.
[14] Santhosh PB,Ulrih NP.Multifunctional superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: promising tools in cancer theranostics. Cancer Lett.2013;336(1):8-17.
[15] Xiong F,Chen Y,Chen J,et al.Rubik-like magnetic nanoassemblies as an efficient drug multifunctional carrier for cancer theranostics.J Control Release.2013;172(3):993-1001.
[16] Chertok B,David AE,Yang VC.Magnetically-enabled and MR-monitored selective brain tumor protein delivery in rats via magnetic nanocarriers.Biomaterials.2011;32(26): 6245-6253.
[17] Yu JH,Li XY,Luo Y,et al.Poly(ethylene glycol) shell-sheddable magnetic nanomicelle as the carrier of doxorubicin with enhanced cellular uptake. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013; 107:213-219.
[18] Chertok B,Moffat BA,David AE,et al.Iron oxide nanoparticles as a drug delivery vehicle for MRI monitored magnetic targeting of brain tumors.Biomaterials.2008;29(4):487-496.
[19] Narayanan S,Sathy BN,Mony U,et al.Biocompatible magnetite/gold nanohybrid contrast agents via green chemistry for MRI and CT bioimaging.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4(1):251-260.
[20] Qu JB,Shao HH,Jing GL,et al.PEG-chitosan-coated iron oxide nanoparticles with high saturated magnetization as carriers of 10-hydroxycamptothecin: preparation, characterization and cytotoxicity studies.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2013;102: 37-44.
[21] Cai H,An X,Cui J,et al.Facile hydrothermal synthesis and surface functionalization of polyethyleneimine-coated iron oxide nanoparticlesfor biomedical applications.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2013;5(5):1722-1731.
[22] Yu J,Li X,Luo Y,et al.Poly(ethylene glycol) shell-sheddable magnetic nanomicelle as the carrier of doxorubicin with enhanced cellularuptake.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013;107:213-219.
[23] Kim J,Kim HS,Lee N,et al.Multifunctional Uniform Nanoparticles Composed of a Magnetite Nanocrystal Core and a Mesoporous Silica Shell for Magnetic Resonance and Fluorescence Imaging and for Drug Delivery.Angew Chem Int Ed.2008;47(44): 8438-8441.
[24] Law WC,Yong KT,Roy I,et al.Optically and Magnetically Doped Organically Modified Silica Nanoparticles as Efficient Magnetically Guided Biomarkers for Two-Photon Imaging of Live Cancer Cells.J Phys Chem C.2008;112(21):7972-7977.
[25] Kempe M,Kempe H,Snowball I,et al.The use of magnetite nanoparticles for implant—assisted magnetic drug targeting in thrombolytic therapy. Biomaterials. 2010; 31(36): 9499-9510.
[26] Teng ZG,Li J,Yan F,et al.Highly magnetizable superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles embedded mesoporous silica spheres and their application for efficient recovery of DNA from agarose gel.J Mater Chem. 2009; 19(13): 1811-1815.
[27] Piao Y,Kim J,Na HB,et al.Wrap-bake-peel process for nanostructural transformation from β-FeOOH nanorods to biocompatible iron oxide nanocapsules.Nat Mater. 2008;7: 242-247.
[28] Kim J,Piao Y,Hyeon T.Multifunctional nanostructured materials for multimodal imaging, and simultaneous imaging and therapy.Chem Soc Rev.2009;38:372-390.
[29] Liu YY, Shi MR, Xu MM,et al.Multifunctional nanoparticles of Fe3O4@SiO2(FITC)/PAH conjugated the recombinant plasmid of pIRSE2-EGFP/VEGF(165) with dual functions for gene delivery and cellular imaging.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2012; 9(10):1197-1207.
[30] Fu R,Jin XM,Liang JL,et al.Preparation of nearly monodispersed Fe3O4/SiO2 composite particles from aggregates of Fe3O4 nanoparticles.J Mater Chem.2011; 21(39): 15352-15356.
[31] Hmori MO,Atijevic EM.Preparation and Properities of uniform coated colloidal Particles. Ⅶ sillica on hematite.J Colloid Interface Sci.1992;150:594. |
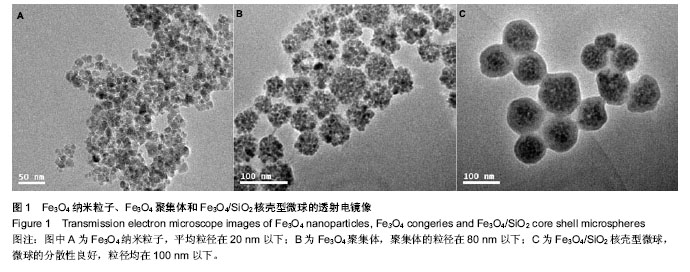
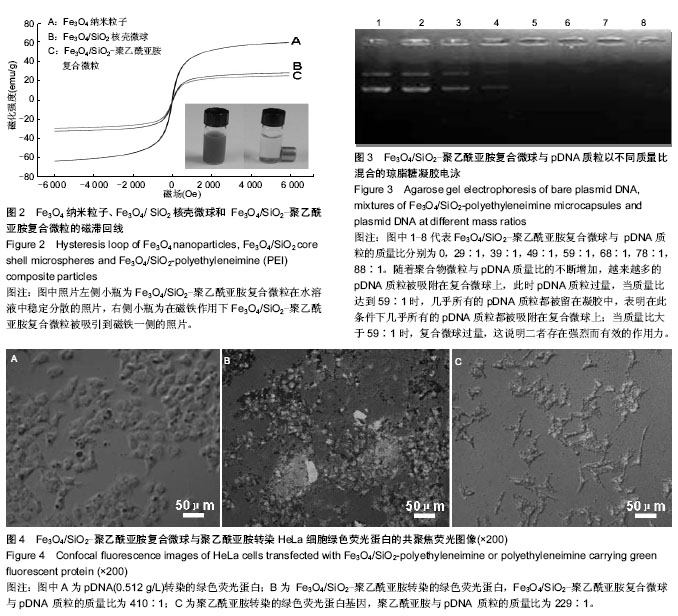
.jpg)